DIP基本思想很简单但很重要:提供复杂逻辑的高级模块应易于重用,并且不受提供实用程序功能的低级模块的更改的影响。 为此,需要引入一种抽象,该抽象将高级模块和低级模块彼此分离。
基于这种想法,Robert C. Martin对依赖倒置原则的定义包括两个部分:
该定义的一个重要细节是,高层和低层模块取决于抽象。设计原理不仅会改变依赖关系的方向。 它通过在高级模块和低级模块之间引入抽象来划分它们之间的依赖关系。因此,最终将获得两个依赖项:
简单来说,Don’t call me, I will call you!这个是一个hollywood principle,所以也叫好莱坞原则。
假如有两种咖啡机,购买者可以在上面制定不同的咖啡,两种咖啡机分别制作两类咖啡:1)基础咖啡 - 通过水和磨碎咖啡混合的过滤咖啡, 2)高级咖啡 - 使用研磨机研磨新鲜的咖啡豆冲泡的咖啡。
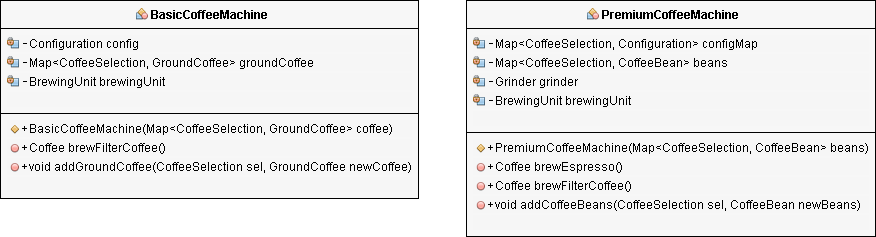
两类咖啡机的应用程序建模为两个类:

BasicCoffeeMachine类制作基础咖啡,包括一个构造器和两个公有方法,其中addGroundCoffee是研磨咖啡, brewFilterCoffee是产生过滤咖啡。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
import java.util.Map;
public class BasicCoffeeMachine implements CoffeeMachine {
private Configuration config;
private Map<CoffeeSelection, GroundCoffee> groundCoffee;
private BrewingUnit brewingUnit;
public BasicCoffeeMachine(Map<CoffeeSelection, GroundCoffee> coffee).
this.groundCoffee = coffee;
this.brewingUnit = new BrewingUnit();
this.config = new Configuration(30, 480);
}
@Override
public Coffee brewFilterCoffee() {
// 获取速溶咖啡
GroundCoffee groundCoffee = this.groundCoffee.get(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE);
// 过滤咖啡
return this.brewingUnit.brew(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE, groundCoffee, this.config.getQuantityWater());
}
public void addGroundCoffee(CoffeeSelection sel, GroundCoffee newCoffee) throws CoffeeException {
GroundCoffee existingCoffee = this.groundCoffee.get(sel);
if (existingCoffee != null) {
if (existingCoffee.getName().equals(newCoffee.getName())) {
existingCoffee.setQuantity(existingCoffee.getQuantity() + newCoffee.getQuantity())
} else {
throw new CoffeeException("Only one kind of coffee supported for each CoffeeSelection.")
}
} else {
this.groundCoffee.put(sel, newCoffee)
}
}
}
也是类似的,不过有两点不同:
public class PremiumCoffeeMachine { private Map<CoffeeSelection, Configuration> configMap; private Map<CoffeeSelection, CoffeeBean> beans; private Grinder grinder private BrewingUnit brewingUnit;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
public PremiumCoffeeMachine(Map<CoffeeSelection, CoffeeBean> beans) {
this.beans = beans;
this.grinder = new Grinder();
this.brewingUnit = new BrewingUnit();
this.configMap = new HashMap<>();
this.configMap.put(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE, new Configuration(30, 480));
this.configMap.put(CoffeeSelection.ESPRESSO, new Configuration(8, 28));
}
public Coffee brewEspresso() {
Configuration config = configMap.get(CoffeeSelection.ESPRESSO);
// 研磨咖啡豆
GroundCoffee groundCoffee = this.grinder.grind(
this.beans.get(CoffeeSelection.ESPRESSO),
config.getQuantityCoffee())
// 冲泡咖啡
return this.brewingUnit.brew(CoffeeSelection.ESPRESSO, groundCoffee,
config.getQuantityWater());
}
public Coffee brewFilterCoffee() {
Configuration config = configMap.get(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE);
// 研磨咖啡豆
GroundCoffee groundCoffee = this.grinder.grind(
this.beans.get(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE),
config.getQuantityCoffee());
// 过滤咖啡
return this.brewingUnit.brew(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE, groundCoffee,
config.getQuantityWater());
}
public void addCoffeeBeans(CoffeeSelection sel, CoffeeBean newBeans) throws CoffeeException {
CoffeeBean existingBeans = this.beans.get(sel);
if (existingBeans != null) {
if (existingBeans.getName().equals(newBeans.getName())) {
existingBeans.setQuantity(existingBeans.getQuantity() + newBeans.getQuantity());
} else {
throw new CoffeeException("Only one kind of coffee supported for each CoffeeSelection.");
}
} else {
this.beans.put(sel, newBeans);
}
} } ``` #### 引入抽象接口 要实现遵循依赖关系反转原理的类并可以使用BasicCoffeeMachine或PremiumCoffeeMachine这个类来冲泡咖啡,需要为两个类引入接口抽象。
这两种咖啡机的主要任务是冲泡咖啡。但是它们可以冲泡不同种类的咖啡。如果使用BasicCoffeeMachine,则只能冲泡过滤咖啡,而使用PremiumCoffeeMachine,则可以冲泡过滤咖啡或浓缩咖啡。那么,哪种接口抽象最适合两个类?
正如所有咖啡爱好者都会同意的那样,过滤咖啡和浓缩咖啡之间存在巨大差异。这就是为什么使用不同的机器来酿造它们的原因,即使如此,有些机器也可以做到。因此,建议创建两个独立的抽象:
public interface EspressoMachine { Coffee brewEspresso(); }
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
####重构BasicCoffeeMachine类
*BasicCoffeeMachine*类制作基础咖啡,所以需要实现*CoffeeMachine*接口
```java
public class BasicCoffeeMachine implements CoffeeMachine {
private Configuration config;
private Map<CoffeeSelection, GroundCoffee> groundCoffee;
private BrewingUnit brewingUnit;
public BasicCoffeeMachine(Map<CoffeeSelection, GroundCoffee> coffee) {
this.groundCoffee = coffee;
this.brewingUnit = new BrewingUnit();
this.config = new Configuration(30, 480);
}
@Override
public Coffee brewFilterCoffee() {
// get the coffee
GroundCoffee groundCoffee = this.groundCoffee.get(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE);
// brew a filter coffee
return this.brewingUnit.brew(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE, groundCoffee, this.config.getQuantityWater());
}
public void addGroundCoffee(CoffeeSelection sel, GroundCoffee newCoffee) throws CoffeeException {
GroundCoffee existingCoffee = this.groundCoffee.get(sel);
if (existingCoffee != null) {
if (existingCoffee.getName().equals(newCoffee.getName())) {
existingCoffee.setQuantity(existingCoffee.getQuantity() + newCoffee.getQuantity());
} else {
throw new CoffeeException("Only one kind of coffee supported for each CoffeeSelection.");
}
} else {
this.groundCoffee.put(sel, newCoffee);
}
}
}
####重构PremiumCoffeeMachine类 需要实现CoffeeMachine接口和EspressoMachine接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class PremiumCoffeeMachine implements CoffeeMachine, EspressoMachine {
private Map<CoffeeSelection, Configuration> configMap;
private Map<CoffeeSelection, CoffeeBean> beans;
private Grinder grinder;
private BrewingUnit brewingUnit;
public PremiumCoffeeMachine(Map<CoffeeSelection, CoffeeBean> beans) {
this.beans = beans;
this.grinder = new Grinder();
this.brewingUnit = new BrewingUnit();
this.configMap = new HashMap<>();
this.configMap.put(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE, new Configuration(30, 480));
this.configMap.put(CoffeeSelection.ESPRESSO, new Configuration(8, 28));
}
@Override
public Coffee brewEspresso() {
Configuration config = configMap.get(CoffeeSelection.ESPRESSO);
// grind the coffee beans
GroundCoffee groundCoffee = this.grinder.grind(
this.beans.get(CoffeeSelection.ESPRESSO),
config.getQuantityCoffee());
// brew an espresso
return this.brewingUnit.brew(CoffeeSelection.ESPRESSO, groundCoffee,
config.getQuantityWater());
}
@Override
public Coffee brewFilterCoffee() {
Configuration config = configMap.get(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE);
// grind the coffee beans
GroundCoffee groundCoffee = this.grinder.grind(
this.beans.get(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE),
config.getQuantityCoffee());
// brew a filter coffee
return this.brewingUnit.brew(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE,
groundCoffee,config.getQuantityWater());
}
public void addCoffeeBeans(CoffeeSelection sel, CoffeeBean newBeans) throws CoffeeException {
CoffeeBean existingBeans = this.beans.get(sel);
if (existingBeans != null) {
if (existingBeans.getName().equals(newBeans.getName())) {
existingBeans.setQuantity(existingBeans.getQuantity() + newBeans.getQuantity());
} else {
throw new CoffeeException("Only one kind of coffee supported for each CoffeeSelection.");
}
} else {
this.beans.put(sel, newBeans);
}
}
}
现在的类图是这样:
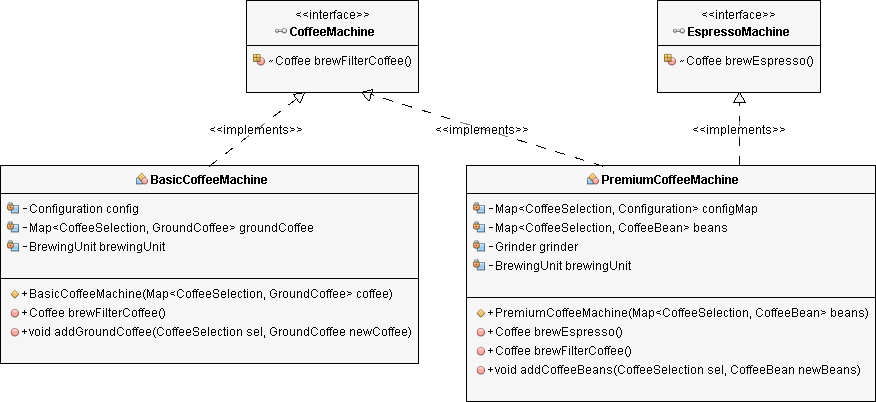
现在,可以创建使用这些接口中的一个或两个来管理咖啡机的其他更高级别的类,而无需直接依赖于任何特定的咖啡机实现。
如下面的代码片段所示,由于CoffeeMachine接口及其提供的功能的抽象,CoffeeApp的实现非常简单。它需要一个CoffeeMachine对象作为构造函数参数,并在prepareCoffee方法中使用它来冲泡一杯过滤咖啡。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class CoffeeApp {
public class CoffeeApp {
private CoffeeMachine coffeeMachine;
public CoffeeApp(CoffeeMachine coffeeMachine) {
this.coffeeMachine = coffeeMachine
}
public Coffee prepareCoffee() throws CoffeeException {
Coffee coffee = this.coffeeMachine.brewFilterCoffee();
System.out.println("Coffee is ready!");
return coffee;
}
}
}
直接依赖于其中一个实现类的代码是CoffeeAppStarter类,这个类实例化CoffeeApp对象并提供CoffeeMachine接口的实现。可以通过使用依赖项注入框架(例如Spring或CDI)在运行时解析依赖项,以此来完全避免这种编译时依赖项。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CoffeeAppStarter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create a Map of available coffee beans
Map<CoffeeSelection, CoffeeBean> beans = new HashMap<CoffeeSelection, CoffeeBean>();
beans.put(CoffeeSelection.ESPRESSO, new CoffeeBean(
"My favorite espresso bean", 1000));
beans.put(CoffeeSelection.FILTER_COFFEE, new CoffeeBean(
"My favorite filter coffee bean", 1000))
// get a new CoffeeMachine object
PremiumCoffeeMachine machine = new PremiumCoffeeMachine(beans);
// Instantiate CoffeeApp
CoffeeApp app = new CoffeeApp(machine);
// brew a fresh coffee
try {
app.prepareCoffee();
} catch (CoffeeException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
DIP引入了上层和下层软件组件之间的接口抽象,以消除它们之间的依赖关系。
如上所示,只需要在代码库中应用“打开/关闭”和“ Liskov替换”原则。 完成此操作后,类也将遵循“依赖倒置原则”。只要不更改任何接口抽象本身,就可以在不影响任何其他类的情况下更改上级和下级组件。