160 - Intersection of Two Linked Lists
原题概述
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists: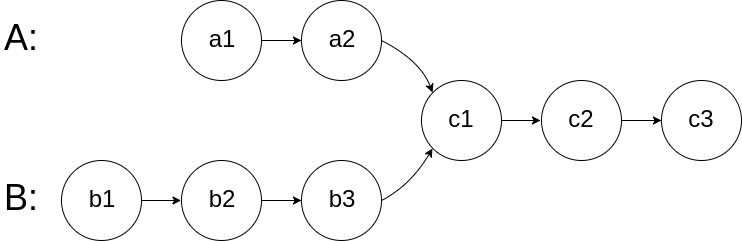
begin to intersect at node c1.
1
2
3
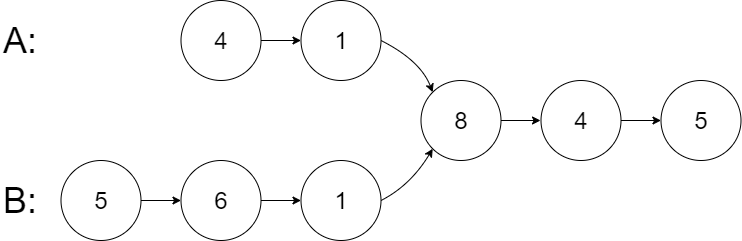
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Reference of the node with value = 8
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,6,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
1
2
3
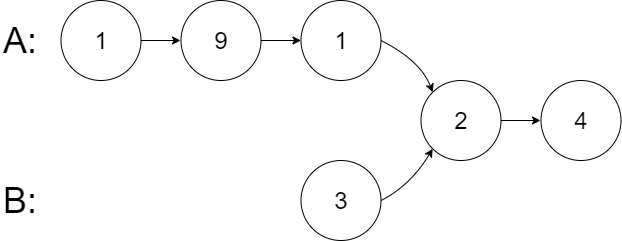
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Reference of the node with value = 2
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [1,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
1
2
3
4
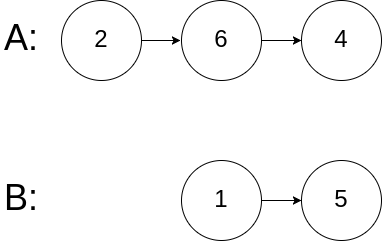
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output: null
Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return
1
null
- The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Each value on each linked list is in the range
1
[1, 10^9]
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
题意和分析
给两个链表,判断是否相交,如果有相交就返回相交的node,没有则相交返回null;不要改变链表的结构,链表中没有环;要求O(n)的时间复杂度和O(1)的空间复杂度。
解题思路有如下:
- 直接循环判断第一个链表的每个节点是否在第二个链表中,如果在第二个中说明相交并返回该node。这种方法的时间复杂度为O(Length(h1) * Length(h2));得找到一种更为有效的方法。
- 针对第一个链表直接构造hash表,然后查询hash表,判断第二个链表的每个节点是否在hash表出现,如果所有的第二个链表的节点都能在hash表中找到,即说明第二个链表与第一个链表有相同的节点。时间复杂度为为线性:O(Length(h1) + Length(h2)),同时为了存储第一个链表的所有节点,空间复杂度为O(Length(h1))。是否还有更好的方法呢,既能够以线性时间复杂度解决问题,又能减少存储空间?
- 如果两个链长度相同的话,那么对应的一个个比下去就能找到,所以只需要把长链表变短即可。 具体算法为:分别遍历两个链表,得到分别对应的长度。然后求长度的差值,把较长的那个链表向后移动这个差值的个数 (跳过较长的List前面的nodes,从长度相等的地方开始一个一个的比较,直到找到Intersection或者到末尾都没有Intersection。),然后一一比较。
- 虽然题目中强调了链表中不存在环,但是我们可以用环的思想来做,我们让两条链表分别从各自的开头开始往后遍历,当其中一条遍历到末尾时,我们跳到另一个条链表的开头继续遍历。两个指针最终会相等,而且只有两种情况,一种情况是在交点处相遇(有交叉),另一种情况是在各自的末尾的空节点(没有交叉)处相等。为什么一定会相等呢,因为两个指针走过的路程相同,是两个链表的长度之和,所以一定会相等。这个方法的时间复杂度是线性的,空间是常数,符合要求。
- 进一步考虑“如果两个没有环的链表相交于某一节点,那么在这个节点之后的所有节点都是两个链表共有的”这个特点,我们可以知道,如果它们相交,则最后一个节点一定是共有的。而我们很容易能得到链表的最后一个节点,所以这成了我们简化解法的一个主要突破口。那么,我们只要判断两个链表的尾指针是否相等。相等,则链表相交;否则,链表不相交。 所以,先遍历第一个链表,记住最后一个节点。然后遍历第二个链表,到最后一个节点时和第一个链表的最后一个节点做比较,如果相同,则相交,否则,不相交。这样我们就得到了一个时间复杂度,它为O((Length(h1) + Length(h2)),而且只用了一个额外的指针来存储最后一个节点。这个方法时间复杂度为线性O(N),空间复杂度为O(1),如果只是判断是否相交这个办法很好,但没有办法知道从哪个node开始相交的。
代码
用办法3减length来做
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
int lenA = getLength(headA), lenB = getLength(headB);
if (lenA > lenB) { //如果headA长,让headA从长度相当于headB的长度开始
for (int i = 0; i < lenA - lenB; ++i) {
headA = headA.next;
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < lenB- lenA; ++i) {//反之从另外一个链表开始
headB = headB.next;
}
}
while (headA != null && headB != null && headA != headB){//挨个比较,看什么时候相同
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
return (headA != null && headB != null) ? headA : null; //return (headA != null && headB != null) ? headB : null;
}
public int getLength(ListNode head){
int count = 0;
while (head != null) {
count++;
head = head.next;
}
return count;
}
}
用办法4环的思想来做(做的路程一样)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode a = headA;
ListNode b = headB;
//对两个链表分别遍历,直到其中一条链表到结尾;结束条件如果相交则一定会在开始重合的节点,
//如果不相交则二者都为null从而跳出循环
while (a != b) {
a = (a == null) ? headB : a.next;
b = (b == null) ? headA : b.next;
}
return a;//return b;
}
}