261 Graph Valid Tree Medium $
You have a graph of 1
n
1
0
1
n - 1
1
edges
1
edges[i] = [ai, bi]
1
ai
1
bi
Return 1
true
1
false
Example 1: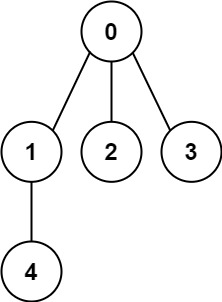
1
2
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,4]]
Output: true
Example 2: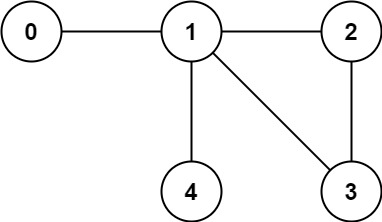
1
2
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[1,3],[1,4]]
Output: false
Constraints:
1
1 <= 2000 <= n
1
0 <= edges.length <= 5000
1
edges[i].length == 2
1
0 <= ai, bi < n
1
ai != bi
- There are no self-loops or repeated edges.
图的DFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
class Solution {
public boolean validTree(int n, int[][] edges) {
// initialize adjacency list
List<List<Integer>> adjList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(n);
// initialize vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
adjList.add(i, new ArrayList<Integer>());
// add edges
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
int u = edges[i][0], v = edges[i][1];
adjList.get(u).add(v);
adjList.get(v).add(u);
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
// make sure there's no cycle
if (hasCycle(adjList, 0, visited, -1))
return false;
// make sure all vertices are connected
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!visited[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
// check if an undirected graph has cycle started from vertex u
boolean hasCycle(List<List<Integer>> adjList, int u, boolean[] visited, int parent) {
visited[u] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < adjList.get(u).size(); i++) {
int v = adjList.get(u).get(i);
if ((visited[v] && parent != v) || (!visited[v] && hasCycle(adjList, v, visited, u)))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
BFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
class Solution {
public boolean validTree(int n, int[][] edges) {
int[] visited = new int[n];
List<List<Integer>> adjList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) { adjList.add(new ArrayList<Integer>()); }
for (int[] edge: edges) {
adjList.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
adjList.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
}
if (hasCycle(-1, 0, visited, adjList)) { return false; } // has cycle
for (int v: visited) { if (v == 0) { return false; } } // not 1 single connected component
return true;
}
private boolean hasCycle(int pred, int vertex, int[] visited, List<List<Integer>> adjList) {
visited[vertex] = 1; // current vertex is being visited
for (Integer succ: adjList.get(vertex)) { // successors of current vertex
if (succ != pred) { // exclude current vertex's predecessor
if (visited[succ] == 1) { return true; } // back edge/loop detected!
else if (visited[succ] == 0) {
if (hasCycle(vertex, succ, visited, adjList)) { return true; }
}
}
}
visited[vertex] = 2;
return false;
}
}
Union-Find with path compression and merge by rank
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
class Solution {
class UnionFind {
int[] parent;
int[] rank;
int count;
UnionFind(int n) {
parent = new int[n];
rank = new int[n];
count = n; // number of components
for (int i=0; i<n; ++i) { parent[i] = i; } // initially, each node's parent is itself.
}
int find(int x) {
if (x != parent[x]) {
parent[x] = find(parent[x]); // find root with path compression
}
return parent[x];
}
boolean union(int x, int y) {
int X = find(x), Y = find(y);
if (X == Y) { return false; }
if (rank[X] > rank[Y]) { parent[Y] = X; } // tree Y is lower
else if (rank[X] < rank[Y]) { parent[X] = Y; } // tree X is lower
else { // same height
parent[Y] = X;
++rank[X];
}
--count;
return true;
}
}
public boolean validTree(int n, int[][] edges) {
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n);
for (int[] edge: edges) {
int x = edge[0], y = edge[1];
if (!uf.union(x, y)) { return false; } // loop detected
}
return uf.count == 1;
}
}