285 Inorder Successor in BST
题目
Given a binary search tree and a node in it, find the in-order successor of that node in the BST.
The successor of a node 1
p
1
p.val
Example 1:
1
2
3
Input: root = [2,1,3], p = 1
Output: 2
Explanation: 1's in-order successor node is 2. Note that both p and the return value is of TreeNode type.
Example 2:
1
2
3
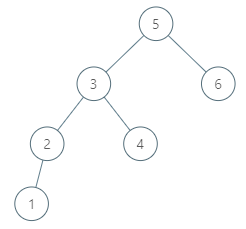
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], p = 6
Output: null
Explanation: There is no in-order successor of the current node, so the answer is null.
Note:
- If the given node has no in-order successor in the tree, return
1
null
- It’s guaranteed that the values of the tree are unique.
分析
中序遍历结果是一个递增的数组,顺序后继是中序遍历中当前节点 之后 最小的节点。
方法1:递归执行中序遍历,获取一个list,在结果list中得到p的下一个。时间O(N),空间O(N)
方法2: 递归执行中序遍历,在递归过程中获取x的下一个。如果当前值是<=x的,那么根据BST的特性只需要在右子树中找。如果当前值>x,则当前值有可能,它的左子树也有可能有更小的但是也>x的,对左子树递归后,选择更接近的(更小的)。时间O(logN),空间O(logN)调用栈的深度。
方法3:方法2的循环实现,如果当前值是<=x的,那么根据BST的特性只需要在右子树中找:cur=cur.right。 如果当前值>x,则当前值有可能,它的左子树也有可能有更小的但是也>x的。则每次走入这个分支时,当前点是一个候选点,记录该节点的值和历史最小节点的值。 时间O(logN),空间O(1)
代码
方法1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<TreeNode> list;
public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
inOrder(root);
TreeNode result = null;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if (list.get(i).val == p.val) {
if (i != list.size() - 1) {
result = list.get(i + 1);
}
}
}
return result;
}
private void inOrder(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
inOrder(node.left);
list.add(node);
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
方法2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
class Solution {
public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {
return inOrder(root, p);
}
private TreeNode inOrder(TreeNode node, TreeNode p) {
if (p == null || node == null) {
return null;
}
if (node.val <= p.val) {//当前和左边都不可能大于p,继续递归右子树
return inOrder(node.right, p);
}
//node > p
TreeNode result = inOrder(node.left, p);
if (result != null && result.val < node.val) {
return result;
} else {
return node;
}
}
}
方法3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
class Solution {
public TreeNode inorderSuccessor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p) {
if (p == null || root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode curr = root;
TreeNode result = null;
while (curr != null) {
if (curr.val <= p.val) {
curr = curr.right;
} else {
if (result == null || result.val > curr.val) {
result = curr;
}
curr = curr.left;
}
}
return result;
}
}