323 Number of Connected Components in an Undirected Graph
题目
You have a graph of 1
n
1
n
1
edges
1
edges[i] = [ai, bi]
1
ai
1
bi
Return the number of connected components in the graph.
Example 1: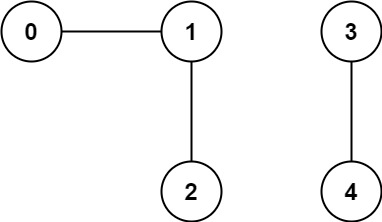
1
2
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: 2
Example 2: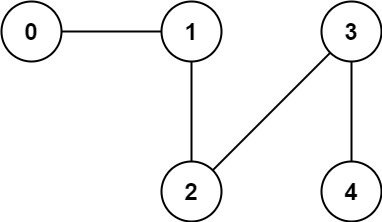
1
2
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4]]
Output: 1
Constraints:
1
1 <= n <= 2000
1
1 <= edges.length <= 5000
1
edges[i].length == 2
1
0 <= ai <= bi < n
1
ai != bi
- There are no repeated edges.
分析
求无向图中的连通分量。跟number of Islands以及Friends Cycle一样,同样也是三种解法:DFS,BFS和Union Find。
代码
DFS,对每一块独立的分量进行深搜
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
class Solution {
public int countComponents(int n, int[][] edges) {
int count = 0;
// 邻接表
List<List<Integer>> adjList = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
adjList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
adjList.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
adjList.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
count++;
dfs(visited, i, adjList);
}
}
return count;
}
private void dfs(boolean[] visited, int index, List<List<Integer>> adjList) {
visited[index] = true;
for (int i : adjList.get(index)) {
if (!visited[i]) {
dfs(visited, i, adjList);
}
}
}
}
BFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
class Solution {
public int countComponents(int n, int[][] edges) {
int count = 0;
//邻接表
List<List<Integer>> adjList = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
adjList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for (int[] edge : edges) {
adjList.get(edge[0]).add(edge[1]);
adjList.get(edge[1]).add(edge[0]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) {
count++;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(i);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int index = queue.poll();
visited[index] = true;
for (int next : adjList.get(index)) {
if (!visited[next]) queue.offer(next);
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
Union Find
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
class Solution {
public int countComponents(int n, int[][] edges) {
int[] parents = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(parents, -1);
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int root1 = find(parents, edge[0]);
int root2 = find(parents, edge[1]);
if (root1 != root2) {
parents[root1] = root2;
n--;
}
}
return n;
}
// 这里并查集只实现find即可,无需union
private int find(int[] parents, int x) {
int root = x;
while (parents[root] != -1) {
root = parents[root];
}
return root;
}
}