490 The Maze
题目
There is a ball in a ‘maze’ with empty spaces (represented as ‘0’) and walls (represented as ‘1’). The ball can go through the empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won’t stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the ‘maze’, the ball’s ‘start’ position and the ‘destination’, where ‘start = [startrow, startcol]’ and ‘destination = [destinationrow, destinationcol]’, return ‘true’ if the ball can stop at the destination, otherwise return ‘false’.
You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls (see examples).
Example 1: 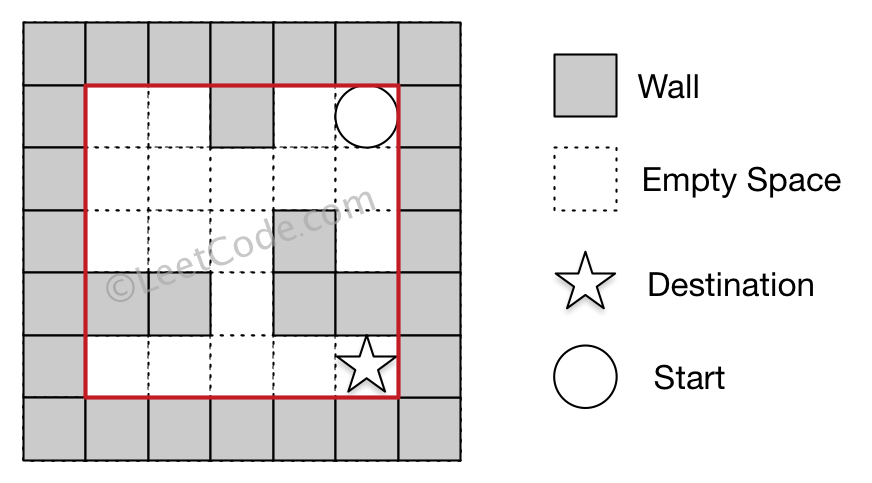
1
2
3
Input: maze = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0],[1,1,0,1,1],[0,0,0,0,0]], start = [0,4], destination = [4,4]
Output: true
Explanation: One possible way is : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right.
Example 2: 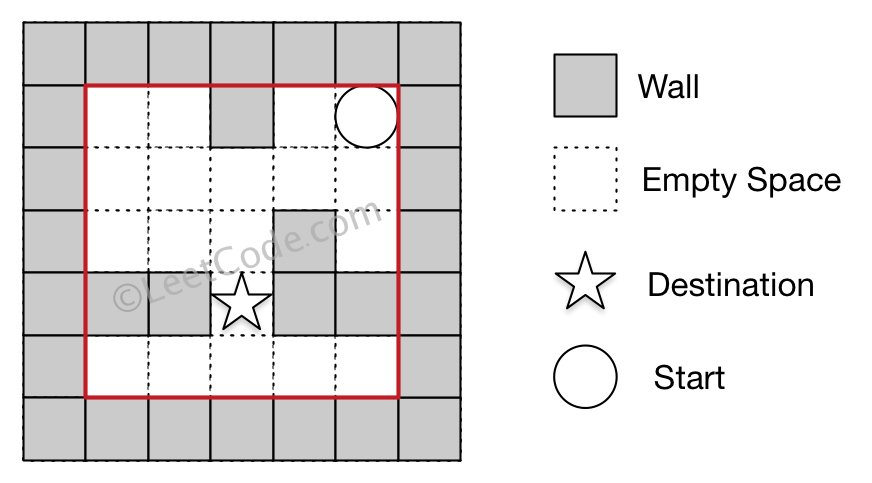
1
2
3
Input: maze = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0],[1,1,0,1,1],[0,0,0,0,0]], start = [0,4], destination = [3,2]
Output: false
Explanation: There is no way for the ball to stop at the destination. Notice that you can pass through the destination but you cannot stop there.
Example 3:
1
2
Input: maze = [[0,0,0,0,0],[1,1,0,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1],[0,1,0,0,0]], start = [4,3], destination = [0,1]
Output: false
Constraints:
- ‘1 <= maze.length, maze[i].length <= 100’
- ‘maze[i][j]’ is ‘0’ or ‘1’.
- ‘start.length == 2’
- ‘destination.length == 2’
- ‘0 <= startrow, destinationrow <= maze.length’
- ‘0 <= startcol, destinationcol <= maze[i].length’
- Both the ball and the destination exist on an empty space, and they will not be at the same position initially.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces.
分析
BFS或者DFS
1) BFS,不是每次走一步,而是一直走
2) DFS
代码
BFS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
class Solution {
int[][] dirs = { {0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0} };
public boolean hasPath(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) {
int rows = maze.length, cols = maze[0].length;
Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
int startPos = start[0] * 100 + start[1], desPos = destination[0] * 100 + destination[1];
queue.offer(startPos);
HashSet<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
visited.add(startPos); // BFS的元素刚访问就要标记,而不是等出栈时再标记,否则会重复访问
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int currPos = queue.poll();
if (currPos == desPos) { //能访问到,拉平后的坐标是不会重复的
return true;
}
visited.add(currPos); //立即标记访问过
int currX = currPos / 100;
int currY = currPos % 100;
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int newX = currX;
int newY = currY;
// 这里并非只走一步,而是只要为0就一直四个方向走,一直到障碍物停止
while (newX >= 0 && newX < rows && newY >= 0 && newY < cols && maze[newX][newY] == 0) {
newX += dir[0];
newY += dir[1];
}
// while循环中是到障碍时停下,这里要从障碍中退出来
newX -= dir[0];
newY -= dir[1];
int newDest = newX * 100 + newY;
// 将障碍物前一个的位置判断并加入到队列中,路程中间的不用加,因为可能重复访问
if (newX >= 0 && newX < rows && newY >= 0 && newY < cols && !visited.contains(newDest)) {
queue.offer(newDest);
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
DFS