1448 Count Good Nodes in Binary Tree
题目
Given a binary tree 1
root
Return the number of good nodes in the binary tree.
Example 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
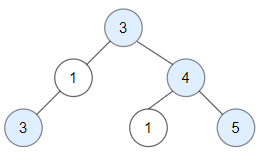
Input: root = [3,1,4,3,null,1,5]
Output: 4
Explanation: Nodes in blue are good.
Root Node (3) is always a good node.
Node 4 -> (3,4) is the maximum value in the path starting from the root.
Node 5 -> (3,4,5) is the maximum value in the path
Node 3 -> (3,1,3) is the maximum value in the path.
Example 2:
1
2
3
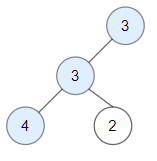
Input: root = [3,3,null,4,2]
Output: 3
Explanation: Node 2 -> (3, 3, 2) is not good, because "3" is higher than it.
Example 3:
1
2
3
Input: root = [1]
Output: 1
Explanation: Root is considered as good.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the binary tree is in the range
1
[1, 10^5]
- Each node’s value is between
1
[-10^4, 10^4]
分析
DFS,topdown
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int result;
public int goodNodes(TreeNode root) {
result = 0;
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
helper(root, root.val); // topdown带个参数下去,因为是全局最大所以也可以做成类变量
return result;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, int max) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
if (root.val >= max) {
result++;
}
max = Math.max(max, root.val);
helper(root.left, max);
helper(root.right, max);
}
}